Program in Scilab:
//Delete the window
clf;
//Declare the variable s and the 'g', 'h' and 'g * h'
s=%s;
g=(s+1)/(s*(s^2+2*s+6));
h=1/(s+1);
gh=g*h;
//Declare the function g*h linear and continuous
ghs=syslin('c',gh)
//ghs2 declare the function as above but with K = 2
ghs2=2*ghs;
//Find the roots of (1 + ghs2)*(s +1)
//, the latter is to cancel the pole with a zero
glc=(1+ghs2)*(s+1);
r=roots(numer(glc))
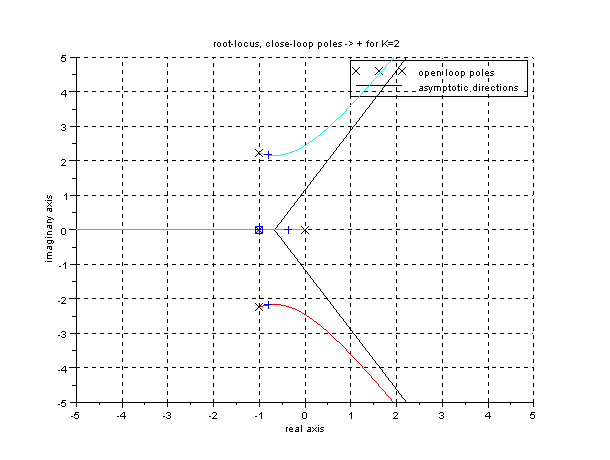
//Draw the root-locus of the function GHS
evans(ghs);
mtlb_axis([-5 5 -5 5])
//We draw the pole and zero are reversed:
plot(-1,0,'o');
plot(-1,0,'x');
//We draw the roots for K = 2;
plot(real(r),imag(r),'+');
xgrid;
xtitle('root-locus, close-loop poles -> + for K=2','real axis',
'imaginary axis');
Resultados
-->r=roots(numer(glc))
r =
- 0.3706383
- 1.
- 0.8146808 + 2.175406i
- 0.8146808 - 2.175406i
|
|